Studio Signal Flow
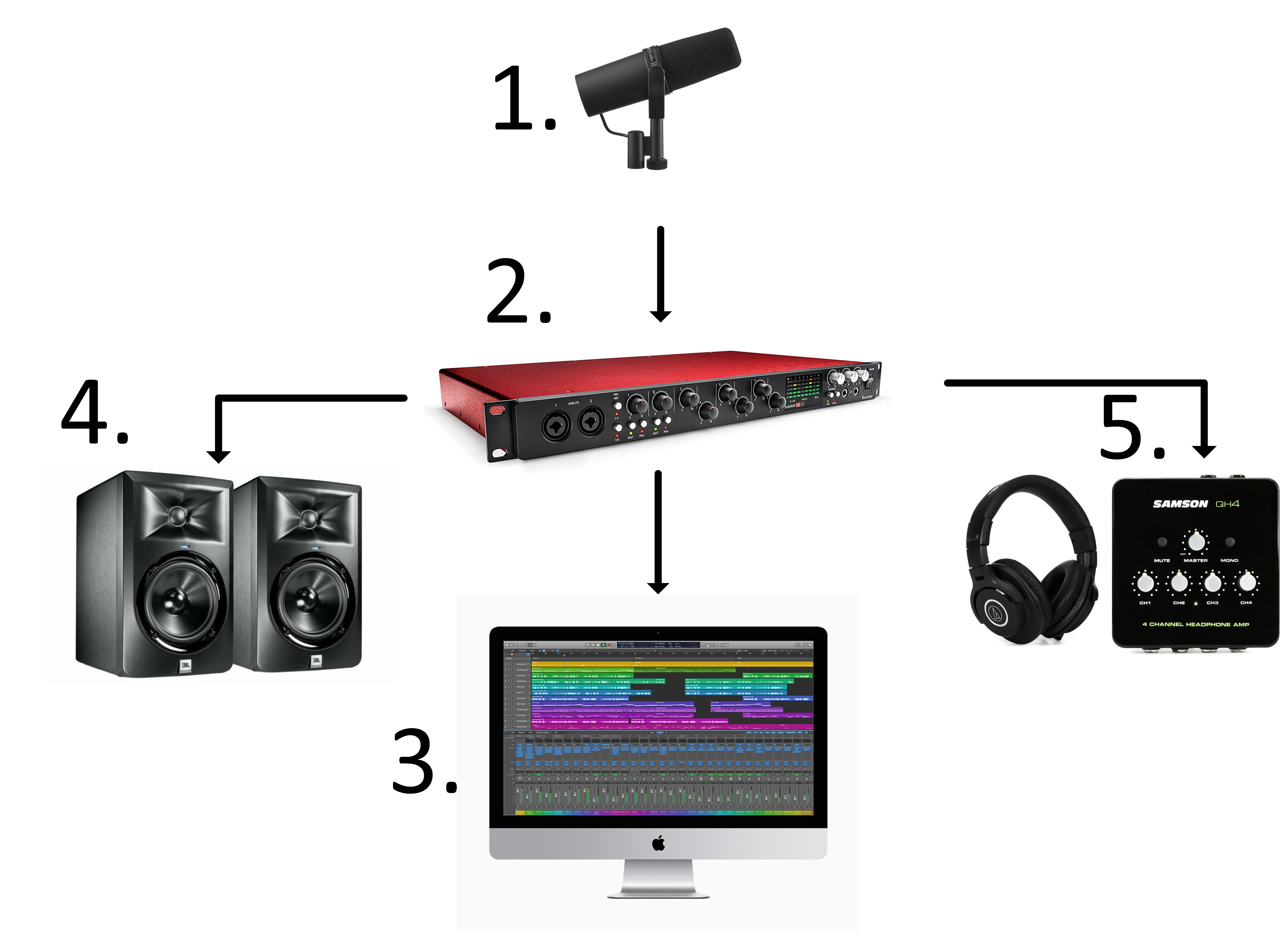
- Microphone
The microphone converts acoustic energy (your voice) into electric energy. This signal is initially captured at a low level and requires being boosted by a device called a microphone preamp.
Some microphones require an additional boost of power from a preamp. This boost is called Phantom Power of 48v. This model of microphone (dynamic) does not require phantom power but we do use a separate device to cleanly boost the signal before the preamp that DOES require phantom power.
- Audio Interface
The audio interface has several important components to it. It acts as a microphone preamp, converts analog audio to digital data and vice versa, routes audio to different outputs, and communicates with your computer and audio software.
- Computer
The Computer hosts the audio software, also knows as a DAW (Digital Audio Workstations) and video editing software. This software is used for recording, editing and mixing projects. The computer communicates with the Audio Interface through the DAW software. It is also where all your project files will be stored unless you decide to use an external hard-drive.
- Studio Monitors
These speakers, typically referred to as monitors in the studio environment, playback audio recorded on the computer. You can control the output volume with Audio Interface. Should only be used for playback during playback and not while recording due to feedback issues.
- Headphones and Headphone Amp
Headphones should be used to monitor audio while recording. The headphone amp can be used to control each speaker’s headphone levels.
